AbleitungsregelSatz Ableitungsregeln
Die wichtigsten Ableitungsregeln im Überblick
Potenzregel
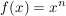
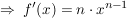
Summenregel
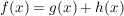
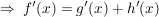
("Die Ableitung einer Summe ist die Summe der Ableitungen.")
Faktorregel
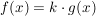
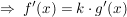
Differenzregel
(Diese Regel ist nicht geläufig, da sie unmittelbar aus Summen- und Faktorregel folgt.)
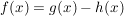
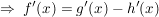
Produktregel
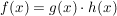
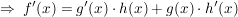
Quotientenregel
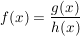
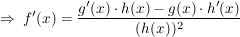
Kettenregel
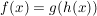
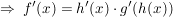
("Innere Ableitung mal äußere Ableitung.")
Umkehrregel für Umkehrfunktionen:
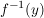 sei die Umkehrfunktion zu y=f(x). sei die Umkehrfunktion zu y=f(x).
Dann gilt:
 oder oder 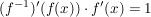
Bemerkungen.
TODO
Beispiele.
Beweis.
Die Beweise finden sich in den einzelnen Artikeln zu den Ableitungsregeln.
|